分布式事务
事务简介
- 事务是用来保证一组数据操作的完整性和一致性
- 事务必须满足ACID的四大特性(待补全)
- 事务具有四种隔离级别(待补全)
- 事务具有七种传播行为(待补全)
什么是分布式事务
分布式事务就是将多个节点的事务看成一个整体处理。
分布式事务由事务参与者、资源服务器、事务管理器等组成,常见例子有,支付、下订单等。
实现思路
两段式事务
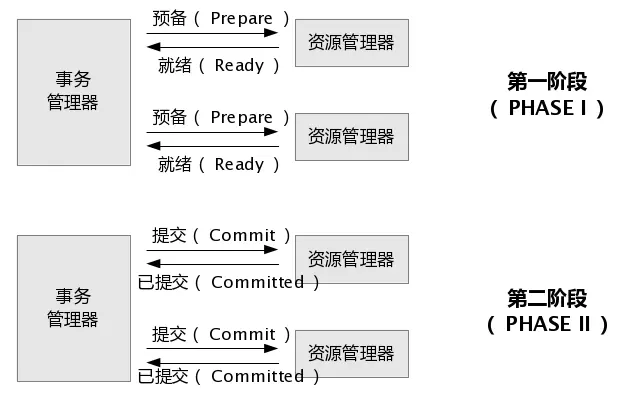
请求阶段:协调者向参与者询问是否可以进行事务提交操作,然后开始等待参与者的响应。
提交阶段:在该阶段,协调者将基于第一个阶段的投票结果进行决策:提交或取消。当且仅当所有的参与者同意提交,事务协调者才通知所有的参与者提交事务,否则协调者将通知所有的参与者回滚事务。
缺点:1)当参与者占有公共资源时,其他第三方节点访问公共资源不得不处于阻塞状态;2)当协调者出错,那么所有的参与者还都处于锁定事务资源的状态中,而无法继续完成事务操作;3)假如在第二阶段中,假如协调者发出commit消息后宕机,接收到这条消息的参与者宕机,此时则无法判断事务状态,无法确定是否已被提交;
三段式事务
事务询问 -> 执行事务预提交 -> 进行事务提交或者事务回滚
降低了参与者的阻塞范围,但引入了新问题:在参与者接收到precommit后,网络出现问题,参与者和协调者无法通行,在这种情况下,参与者依然会执行事务的提交。
基于XA的分布式事务
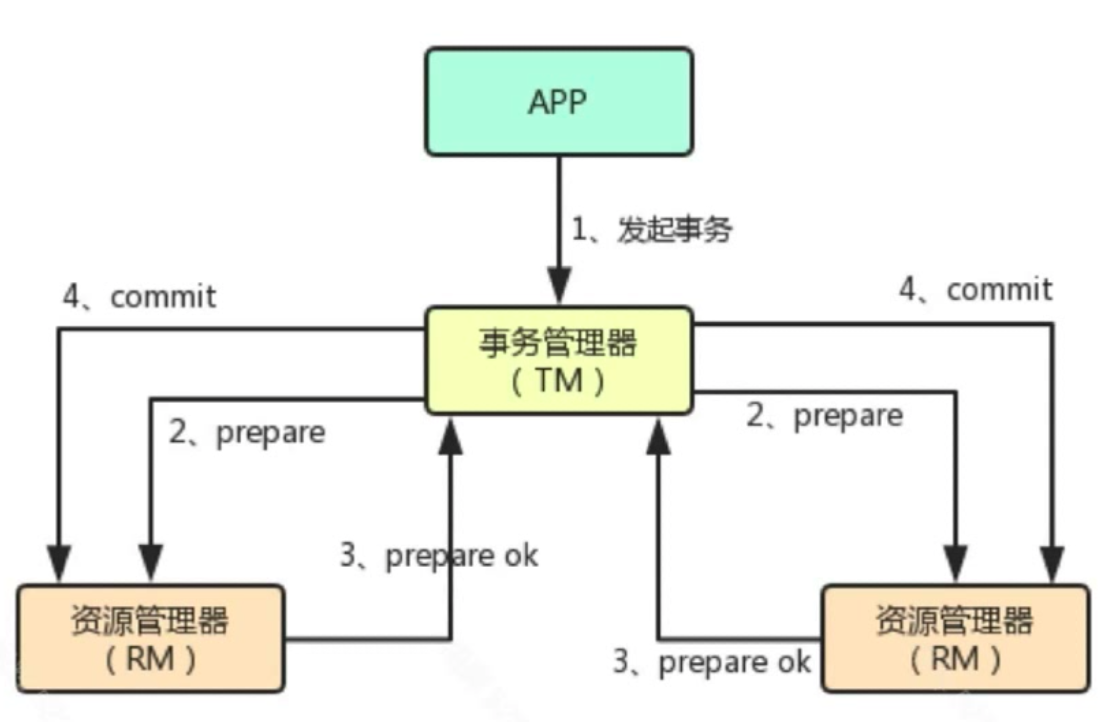
缺点:1)性能较差;2)很多nosql不支持XA协议;
基于消息的最终一致性方案
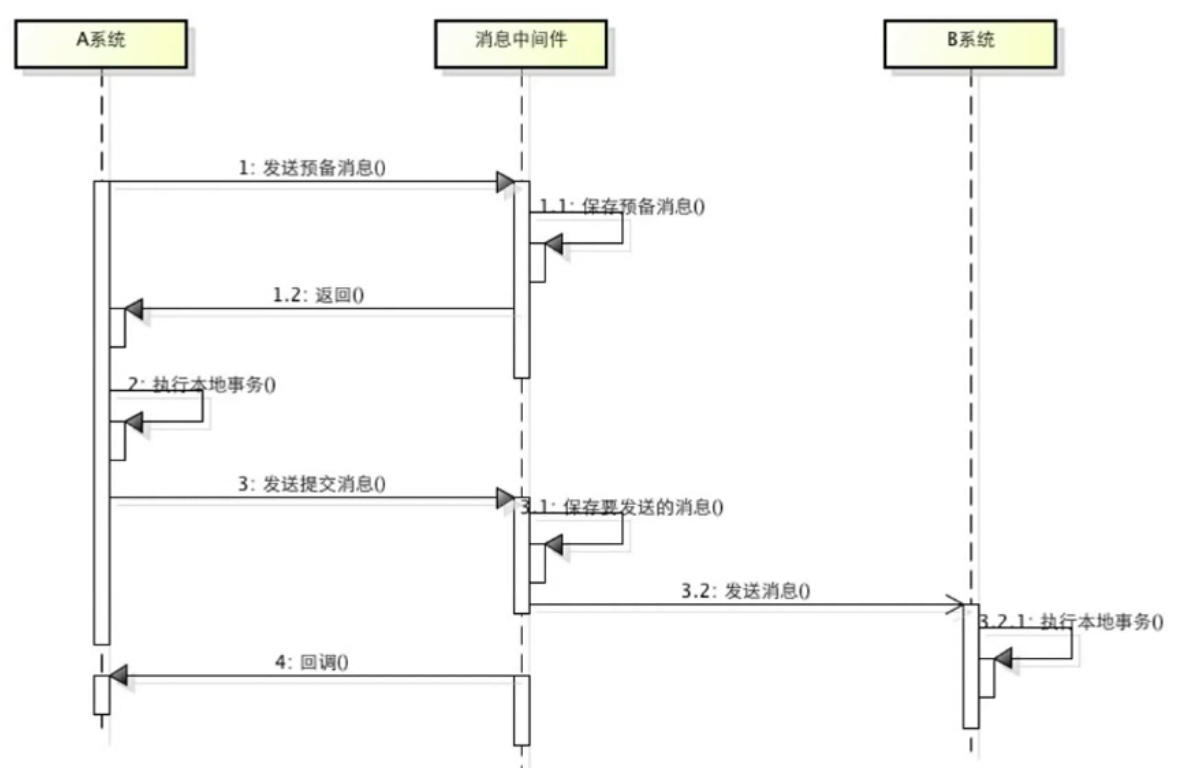
缺点:属于强一致性事务,会存在资源浪费
TCC编程式补偿性事务
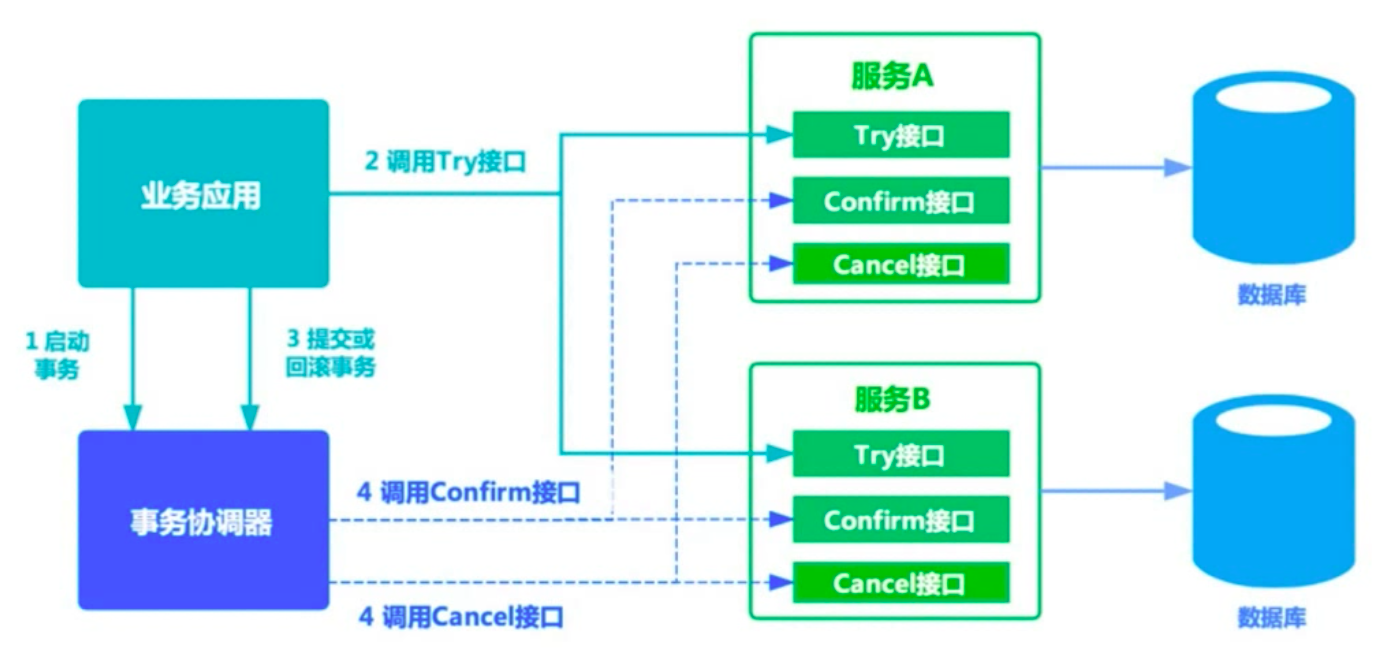
TCC事务是柔性事务,在try阶段要对资源做预留,在confirm或cancel阶段释放资源,与基于消息事务对比,TCC的时效性更好。
TCC模型是把锁的粒度完全交给业务处理,它分为三个阶段:
- Try阶段主要是对业务系统做检测及资源预留;
- 如果try阶段所有业务资源都预留成功,则执行confirm,否则执行cancel;
- confirm:不做任务业务检查,仅使用预留的资源执行业务操作,失败会重试;
- cancel:取消执行业务操作,释放预留的资源,失败会重试;
举例
以简单的电商系统为例,小明在淘宝上花100元买了一本书,获赠10个积分,产生如下操作:
- 订单系统创建商品订单;
- 支付系统接受小明的支付;
- 库存系统扣减产品库存;
- 会员系统给小明账户增加会员积分;
这几个动作需要作为一个事务执行,要同时成功或者同时撤销。如果采用TCC事务模式,那么各个系统需要改造为如下状态:
1)订单系统
try:创建一个订单,状态显示为“待支付”;
confirm:更新订单的状态为“已完成”;
cancel:更新订单的状态为“已取消”;
2)支付系统
try:假设小明账户中有1000元,冻结小明账户中的100元,此时小明看到的余额依然是1000元;
confirm:将账户余额变为900元,并清除冻结记录;
concel:清除冻结记录;
3)库存系统
try:假设库存中还生10本书,冻结其中的一本书,现实库存依然有10本书;
confirm:将剩余库存更新为9本书,并清除冻结记录;
cancel:清除冻结记录;
4)会员系统
try:假设小明原因积分为3000,给小明账户预增加10积分,账户显示的积分依然是3000分;
confirm:将账户积分更新为3010,并清除预增加记录;
cancel:清除预增加记录;
缺点:TCC 事务模型对业务方侵入较大,需要业务方把功能的实现上由一个接口拆分为三个,开发成本较高。
同时 TCC 事务为了解决异步网络中的通信失败或超时带来的异常情况,要求业务方在设计实现上要遵循三个策略:
允许空回滚:原因是异常发生在阶段 1 时,部分参与方没有收到 try 请求从而触发整个事务的 cancel 操作,try 失败或者没有执行 try 操作的参与方收到 cancel 请求时,要进行空回滚操作;
保持幂等性:原因是异常发生在阶段 2 时,比如网络超时,则会重复调用参与方的 confirm/cancel 方法,因此需要这两个方法实现上保证幂等性;
防止资源悬挂:原因网络异常导致两个阶段无法保证严格的顺序执行,出现参与方侧 try 请求比 cancel 请求更晚到达的情况,cancel 会执行空回滚而确保事务的正确性,但是此时 try 方法也不可以再被执行;
分布式事务框架
TCC-Transaction分析
仓库:https://github.com/changmingxie/tcc-transaction
使用方法
- 在需要提供分布式事务支持的接口方法上添加
@Compensable;
- 在对应的接口实现方法上也添加 @Compensable,并添加注解参数
confirmMethod, cancelMethod 和 transactionContextEditor;
- 实现对应的
confirmMethod 和 cancelMethod(必须和 try 方法在同一个类中);
注意:
- 在分布式事务框架中,不要轻易在业务层捕获所有异常,只有在抛出异常的情况下,分布式事务框架才知道该业务是执行失败的,继而执行
cancelMethod;
- 使用 TCC-Transaction 时,confirm 和 cancel 的幂等性问题需要人为代码保证;
- TCC 的数据库应该和业务数据库分开,以保证分布式事务的正常进行;
源码分析
tcc的事务并不是数据库的事务,而是应用层的事务,Transaction如下:
public class Transaction implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7291423944314337931L;
private TransactionXid xid;
private TransactionStatus status;
private TransactionType transactionType;
private volatile int retriedCount = 0;
private Date createTime = new Date();
private Date lastUpdateTime = new Date();
private long version = 1;
private List<Participant> participants = new ArrayList<Participant>();
private Map<String, Object> attachments = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>();
...
}
|
CompensableTransactionAspect是一个AOP切面类,@Pointcut 将 @Compensable 注解标记为切入点,其签名为compensableService()。@Around 表示在compensableService()之前和之后调用 interceptCompensableMethod()。
@Aspect
public abstract class CompensableTransactionAspect {
private CompensableTransactionInterceptor compensableTransactionInterceptor;
public void setCompensableTransactionInterceptor(CompensableTransactionInterceptor compensableTransactionInterceptor) {
this.compensableTransactionInterceptor = compensableTransactionInterceptor;
}
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.mengyun.tcctransaction.api.Compensable)")
public void compensableService() {
}
@Around("compensableService()")
public Object interceptCompensableMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
return compensableTransactionInterceptor.interceptCompensableMethod(pjp);
}
public abstract int getOrder();
}
|
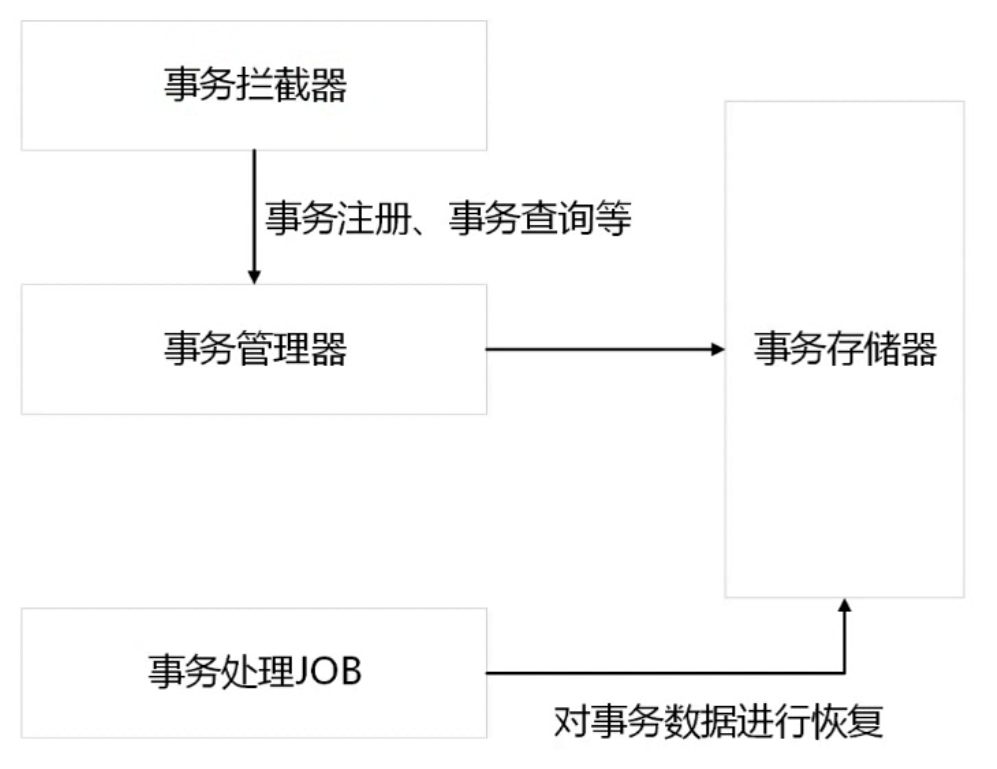
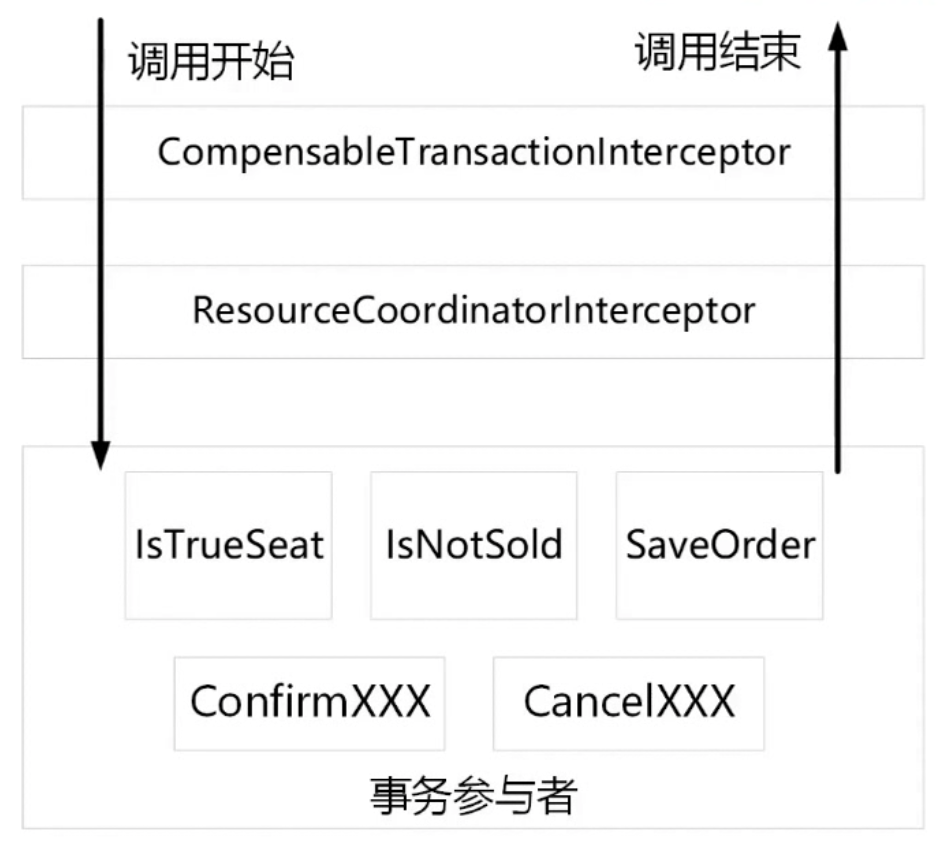
CompensableTransactionInterceptor是事务拦截器,具有以下作用:
- 将事务区分为ROOT事务和PROVIDER分支事务;
- 不断地修改数据库内的状态(初始化事务、修改事务状态);
- 修改和清除事务管理区中的事务队列;
- 并没有执行目标对象方法,pjp.proceed() 其实是交给了下一个拦截器 ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor;
public class CompensableMethodContext {
ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = null;
Method method = null;
Compensable compensable = null;
Propagation propagation = null;
TransactionContext transactionContext = null;
public CompensableMethodContext(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
this.pjp = pjp;
this.method = getCompensableMethod();
this.compensable = method.getAnnotation(Compensable.class);
this.propagation = compensable.propagation();
this.transactionContext = FactoryBuilder.factoryOf(compensable.transactionContextEditor()).getInstance().get(pjp.getTarget(), method, pjp.getArgs());
}
...
}
public class CompensableTransactionInterceptor {
public Object interceptCompensableMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
CompensableMethodContext compensableMethodContext = new CompensableMethodContext(pjp);
boolean isTransactionActive = transactionManager.isTransactionActive();
if (!TransactionUtils.isLegalTransactionContext(isTransactionActive, compensableMethodContext)) {
throw new SystemException("no active compensable transaction while propagation is mandatory for method " + compensableMethodContext.getMethod().getName());
}
switch (compensableMethodContext.getMethodRole(isTransactionActive)) {
case ROOT:
return rootMethodProceed(compensableMethodContext);
case PROVIDER:
return providerMethodProceed(compensableMethodContext);
default:
return pjp.proceed();
}
}
private Object rootMethodProceed(CompensableMethodContext compensableMethodContext) throws Throwable {
Object returnValue = null;
Transaction transaction = null;
boolean asyncConfirm = compensableMethodContext.getAnnotation().asyncConfirm();
boolean asyncCancel = compensableMethodContext.getAnnotation().asyncCancel();
Set<Class<? extends Exception>> allDelayCancelExceptions = new HashSet<Class<? extends Exception>>();
allDelayCancelExceptions.addAll(this.delayCancelExceptions);
allDelayCancelExceptions.addAll(Arrays.asList(compensableMethodContext.getAnnotation().delayCancelExceptions()));
try {
transaction = transactionManager.begin(compensableMethodContext.getUniqueIdentity());
try {
returnValue = compensableMethodContext.proceed();
} catch (Throwable tryingException) {
if (!isDelayCancelException(tryingException, allDelayCancelExceptions)) {
logger.warn(String.format("compensable transaction trying failed. transaction content:%s", JSON.toJSONString(transaction)), tryingException);
transactionManager.rollback(asyncCancel);
}
throw tryingException;
}
transactionManager.commit(asyncConfirm);
} finally {
transactionManager.cleanAfterCompletion(transaction);
}
return returnValue;
}
private Object providerMethodProceed(CompensableMethodContext compensableMethodContext) throws Throwable {
Transaction transaction = null;
boolean asyncConfirm = compensableMethodContext.getAnnotation().asyncConfirm();
boolean asyncCancel = compensableMethodContext.getAnnotation().asyncCancel();
try {
switch (TransactionStatus.valueOf(compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext().getStatus())) {
case TRYING:
transaction = transactionManager.propagationNewBegin(compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext());
return compensableMethodContext.proceed();
case CONFIRMING:
try {
transaction = transactionManager.propagationExistBegin(compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext());
transactionManager.commit(asyncConfirm);
} catch (NoExistedTransactionException excepton) {
}
break;
case CANCELLING:
try {
transaction = transactionManager.propagationExistBegin(compensableMethodContext.getTransactionContext());
transactionManager.rollback(asyncCancel);
} catch (NoExistedTransactionException exception) {
}
break;
}
} finally {
transactionManager.cleanAfterCompletion(transaction);
}
Method method = compensableMethodContext.getMethod();
return ReflectionUtils.getNullValue(method.getReturnType());
}
private boolean isDelayCancelException(Throwable throwable, Set<Class<? extends Exception>> delayCancelExceptions) {
if (delayCancelExceptions != null) {
for (Class delayCancelException : delayCancelExceptions) {
Throwable rootCause = ExceptionUtils.getRootCause(throwable);
if (delayCancelException.isAssignableFrom(throwable.getClass())
|| (rootCause != null && delayCancelException.isAssignableFrom(rootCause.getClass()))) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
|
TransactionManager
public class TransactionManager {
private TransactionRepository transactionRepository;
private static final ThreadLocal<Deque<Transaction>> CURRENT = new ThreadLocal<Deque<Transaction>>();
private ExecutorService executorService;
...
public Transaction begin(Object uniqueIdentify) {
Transaction transaction = new Transaction(uniqueIdentify,TransactionType.ROOT);
transactionRepository.create(transaction);
registerTransaction(transaction);
return transaction;
}
public Transaction propagationNewBegin(TransactionContext transactionContext) {
Transaction transaction = new Transaction(transactionContext);
transactionRepository.create(transaction);
registerTransaction(transaction);
return transaction;
}
public Transaction propagationExistBegin(TransactionContext transactionContext) throws NoExistedTransactionException {
Transaction transaction = transactionRepository.findByXid(transactionContext.getXid());
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.changeStatus(TransactionStatus.valueOf(transactionContext.getStatus()));
registerTransaction(transaction);
return transaction;
} else {
throw new NoExistedTransactionException();
}
}
public void commit(boolean asyncCommit) {
final Transaction transaction = getCurrentTransaction();
transaction.changeStatus(TransactionStatus.CONFIRMING);
transactionRepository.update(transaction);
if (asyncCommit) {
try {
Long statTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
commitTransaction(transaction);
}
});
logger.debug("async submit cost time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - statTime));
} catch (Throwable commitException) {
logger.warn("compensable transaction async submit confirm failed, recovery job will try to confirm later.", commitException);
throw new ConfirmingException(commitException);
}
} else {
commitTransaction(transaction);
}
}
private void commitTransaction(Transaction transaction) {
try {
transaction.commit();
transactionRepository.delete(transaction);
} catch (Throwable commitException) {
logger.warn("compensable transaction confirm failed, recovery job will try to confirm later.", commitException);
throw new ConfirmingException(commitException);
}
}
public void rollback(boolean asyncRollback) {
final Transaction transaction = getCurrentTransaction();
transaction.changeStatus(TransactionStatus.CANCELLING);
transactionRepository.update(transaction);
if (asyncRollback) {
try {
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
rollbackTransaction(transaction);
}
});
} catch (Throwable rollbackException) {
logger.warn("compensable transaction async rollback failed, recovery job will try to rollback later.", rollbackException);
throw new CancellingException(rollbackException);
}
} else {
rollbackTransaction(transaction);
}
}
private void registerTransaction(Transaction transaction) {
if (CURRENT.get() == null) {
CURRENT.set(new LinkedList<Transaction>());
}
CURRENT.get().push(transaction);
}
public void cleanAfterCompletion(Transaction transaction) {
if (isTransactionActive() && transaction != null) {
Transaction currentTransaction = getCurrentTransaction();
if (currentTransaction == transaction) {
CURRENT.get().pop();
if (CURRENT.get().size() == 0) {
CURRENT.remove();
}
} else {
throw new SystemException("Illegal transaction when clean after completion");
}
}
}
...
}
|
ResourceCoordinatorAspect:主要是为了设置事务的参与者
@Aspect
public abstract class ResourceCoordinatorAspect {
private ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor resourceCoordinatorInterceptor;
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.mengyun.tcctransaction.api.Compensable)")
public void transactionContextCall() {
}
@Around("transactionContextCall()")
public Object interceptTransactionContextMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
return resourceCoordinatorInterceptor.interceptTransactionContextMethod(pjp);
}
public void setResourceCoordinatorInterceptor(ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor resourceCoordinatorInterceptor) {
this.resourceCoordinatorInterceptor = resourceCoordinatorInterceptor;
}
public abstract int getOrder();
}
|
ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor:主要处理 try 阶段的事情,在 try 阶段,就将所有的“资源”封装完成并交给事务管理器。然后事务管理器修改数据库状态。
“资源”指“事务资源”,即事务的参与者:confirm上下文,cancel上下文,分支事务信息。
public class ResourceCoordinatorInterceptor {
private TransactionManager transactionManager;
public void setTransactionManager(TransactionManager transactionManager) {
this.transactionManager = transactionManager;
}
public Object interceptTransactionContextMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Transaction transaction = transactionManager.getCurrentTransaction();
if (transaction != null) {
switch (transaction.getStatus()) {
case TRYING:
enlistParticipant(pjp);
break;
case CONFIRMING:
break;
case CANCELLING:
break;
}
}
return pjp.proceed(pjp.getArgs());
}
private void enlistParticipant(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Method method = CompensableMethodUtils.getCompensableMethod(pjp);
if (method == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("join point not found method, point is : %s", pjp.getSignature().getName()));
}
Compensable compensable = method.getAnnotation(Compensable.class);
String confirmMethodName = compensable.confirmMethod();
String cancelMethodName = compensable.cancelMethod();
Transaction transaction = transactionManager.getCurrentTransaction();
TransactionXid xid = new TransactionXid(transaction.getXid().getGlobalTransactionId());
if (FactoryBuilder.factoryOf(compensable.transactionContextEditor()).getInstance().get(pjp.getTarget(), method, pjp.getArgs()) == null) {
FactoryBuilder.factoryOf(compensable.transactionContextEditor()).getInstance().set(new TransactionContext(xid, TransactionStatus.TRYING.getId()), pjp.getTarget(), ((MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature()).getMethod(), pjp.getArgs());
}
Class targetClass = ReflectionUtils.getDeclaringType(pjp.getTarget().getClass(), method.getName(), method.getParameterTypes());
InvocationContext confirmInvocation = new InvocationContext(targetClass,
confirmMethodName,
method.getParameterTypes(), pjp.getArgs());
InvocationContext cancelInvocation = new InvocationContext(targetClass,
cancelMethodName,
method.getParameterTypes(), pjp.getArgs());
Participant participant =
new Participant(
xid,
confirmInvocation,
cancelInvocation,
compensable.transactionContextEditor());
transactionManager.enlistParticipant(participant);
}
}
|
此时经过两个拦截器后,才调用到目标对象方法,即对应try逻辑的被切方法。






